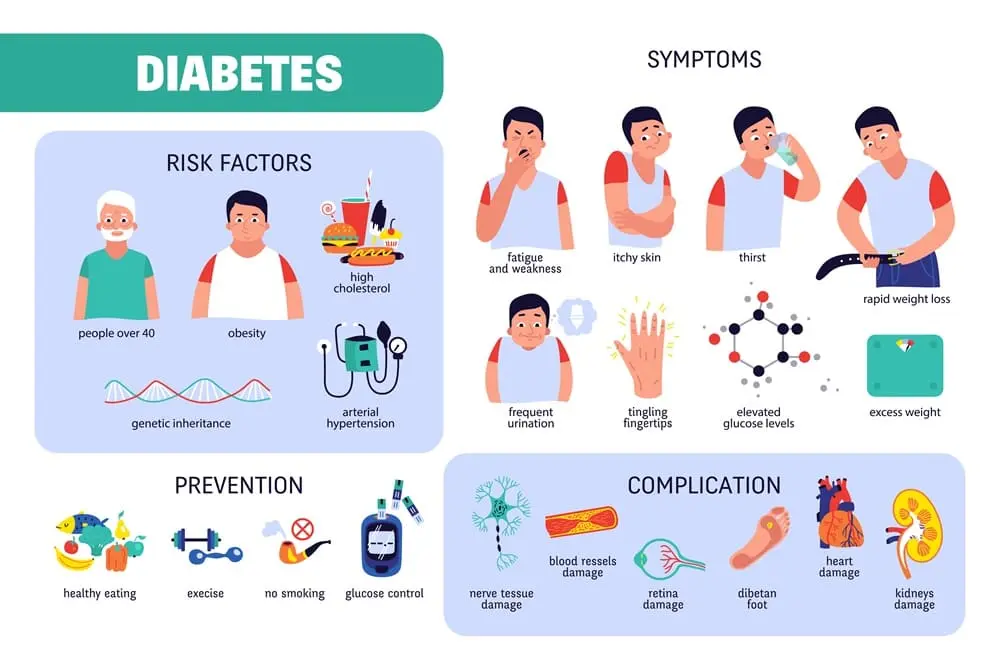
Symptoms and Signs of Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels. Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to timely diagnosis and effective management of the disease. This article explores the various signs of diabetes, including both common and less-known indicators, to help you stay informed about your health.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes occurs when the body either cannot produce enough insulin (a hormone that regulates blood sugar) or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. This results in elevated blood sugar levels, which can lead to serious health complications if left untreated.
Common Symptoms of Diabetes
Increased Thirst and Urination: Excessive thirst (polydipsia) and frequent urination (polyuria) are classic symptoms of diabetes. High blood sugar levels cause the kidneys to work harder to filter and absorb excess sugar. This process leads to increased urination, which in turn causes dehydration and triggers thirst.
Extreme Hunger: Despite eating regularly, individuals with diabetes may experience persistent hunger (polyphagia). This is because the body’s cells are not receiving enough glucose, despite high blood sugar levels, due to insulin deficiency or resistance.
Unexplained Weight Loss: Rapid and unexplained weight loss can occur in individuals with type 1 diabetes, where the body does not produce insulin. Without insulin, the body begins to break down muscle and fat for energy, leading to weight loss.
Fatigue: Diabetes can cause fatigue and a general feeling of being tired all the time. This is due to the body’s inability to properly convert glucose into energy.
Blurred Vision: High blood sugar levels can affect the fluid levels in the eyes, leading to blurred vision. This symptom usually resolves once blood sugar levels are controlled.
Slow Healing of Wounds: Diabetes can impair the body’s ability to heal wounds and infections. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and affect circulation, delaying the healing process.
Frequent Infections: Individuals with diabetes may be more prone to infections, especially yeast infections (such as thrush) and urinary tract infections (UTIs). High blood sugar levels provide a favorable environment for bacteria and fungi to grow.
Less Common Signs of Diabetes
Dry, Itchy Skin: Poor circulation and high blood sugar levels can lead to dry, itchy skin, especially on the hands and feet.
Tingling or Numbness: Diabetes can cause nerve damage (neuropathy) due to high blood sugar levels. Tingling, numbness, or burning sensations in the hands, arms, legs, or feet are common symptoms.
Yeast Infections: Women with diabetes may experience frequent yeast infections, often due to elevated blood sugar levels providing a breeding ground for yeast.
Gum Problems: Diabetes increases the risk of gum disease and infections. Swollen, red, or bleeding gums may indicate poorly controlled blood sugar levels.
Gestational Diabetes Symptoms
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy when the body cannot produce enough insulin to meet the increased needs. Symptoms may include:
Increased Thirst and Urination: Similar to other types of diabetes, gestational diabetes can cause excessive thirst and frequent urination.
Fatigue: Feeling tired despite adequate rest can be a sign of gestational diabetes.
Blurred Vision: Vision changes may occur due to fluctuating blood sugar levels.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience any symptoms of diabetes, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider promptly for testing and diagnosis. Early detection and management can help prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Risk Factors for Diabetes
Several factors increase the risk of developing diabetes, including:
- Family History: A family history of diabetes increases your risk.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese is a significant risk factor, particularly for type 2 diabetes.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Sedentary lifestyles contribute to insulin resistance and increase the risk of diabetes.
- Age: The risk of type 2 diabetes increases with age, especially after 45 years.
Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans, Hispanic/Latino Americans, Native Americans, and Asian Americans, have a higher risk of diabetes.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis typically involves blood tests to measure blood sugar levels. Treatment varies depending on the type of diabetes diagnosed:
- Type 1 Diabetes: Managed with insulin therapy, regular blood sugar monitoring, a balanced diet, and exercise.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Initially managed with lifestyle modifications, including diet and exercise. Medications and insulin therapy may be necessary as the disease progresses.
Gestational Diabetes: Managed with diet, exercise, and sometimes insulin therapy during pregnancy to keep blood sugar levels under control.
Lifestyle Tips for Managing Diabetes
Healthy Eating: Follow a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit sugar, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats.
Regular Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling.
Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: Regularly monitor blood sugar levels as recommended by your healthcare provider. Keep a record of your readings.
Medication Adherence: Take prescribed medications as directed and attend regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare team.
Manage Stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
Conclusion
Recognizing the symptoms and signs of diabetes is crucial for early detection and effective management. If you experience any symptoms, consult your healthcare provider for proper testing and diagnosis. With timely intervention and lifestyle modifications, individuals with diabetes can lead healthy, fulfilling lives while minimizing the risk of complications associated with the condition. Taking proactive steps towards managing diabetes improves overall health and well-being.