Hives
What are hives?
Hives, which are also called urticaria, are itchy, raised bumps on the skin. Most of the time, they are red, pink, or flesh-colored, and they can sting or hurt. Most of the time, hives are caused by an allergic reaction to a drug or food or a reaction to something in the environment that irritates the skin.
Most of the time, hives are a short-term problem that can be helped with allergy medicine. Most rashes clear up by themselves. But cases that don’t go away and hives that come with a severe allergic reaction are bigger medical concerns.18
What causes hives?
Most of the time, hives are caused by an allergic reaction to something you touched or ate. When you have an allergic reaction, your body starts to put chemicals into your blood called histamines. Histamines are chemicals that your body makes to fight off infections and other threats from the outside world. Unfortunately, the histamines can make some people swell up, itch, and have many of the other symptoms of hives. In terms of allergens, pollen, medications, food, animal dander, and insect bites can all cause hives.
Hives can also be brought on by things other than allergies. People often get hives because they are stressed, are wearing tight clothes, are exercising, are sick, or have an infection. You can also get hives if you spend too much time in hot or cold temperatures or if you sweat too much and irritate your skin. Since there are many things that could cause hives, it is often hard to figure out what caused them.
Who is at risk?
Hives are more likely to happen to people who have allergies. You may also get hives if you take certain medicines or if you accidentally come into contact with things you may be allergic to, like food or pollen. If you already have an infection or other health problem, you might be more likely to get hives.
What do hives look like?
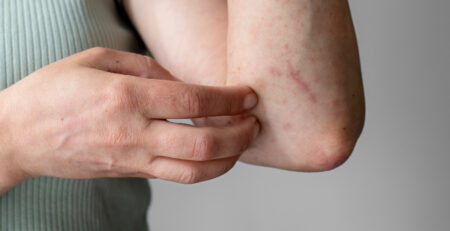
The welts that show up on the skin are the most obvious sign that you have hives. Welts can be red, but they can also be the same colour as your skin. They can be small and round, shaped like rings, or big and all different sizes and shapes. Hives are itchy and tend to show up in groups on the part of the body they are on. They can get bigger, change form, and spread out.
During the outbreak, hives may come and go or come back. Each hive can last anywhere from 30 minutes to a whole day. When you press on hives, they may turn white. The hives may change shape or grow together to make a larger, raised area.
There are many places on the body where hives can happen. If you get hives around your throat or on your tongue, or if they make it hard for you to breathe, call 911 or go to the hospital right away.
Types of hives
Allergic Reactions
Most of the time, hives are caused by allergic reactions. These can be brought on by any allergen to which you might be sensitive, such as:
- foods (such as nuts, milk, and eggs)
- pet dander
- pollen
- dust mites
- insect bites or stings
- medications (primarily antibiotics, cancer drugs, and ibuprofen)
Mild cases of hives caused by allergies are usually treated with long-term or short-term allergy medications and by avoiding the trigger.
Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction that can kill you. When this happens, people often have trouble breathing, feel sick or throw up, swell up a lot, and feel dizzy. If you think someone is having anaphylaxis, call 911 right away.
Chronic hives
Chronic hives are ones that last for a long time and don’t always have a clear cause. This condition, which is also called chronic urticaria, is marked by recurring hives that can get in the way of your life. The Mayo Clinic says that these can last anywhere from six weeks to several months or even years.
If you have welts that don’t go away in six weeks, you may have chronic hives. Even though this kind of hives is not dangerous, it can be painful and hard to treat. They could also be signs of a bigger health problem, like:
- celiac disease
- lupus
- type 1 diabetes
- rheumatoid arthritis
- thyroid disease
Dermatographism
This kind of severe hives isn’t too bad. It’s caused by scratching too much or putting constant pressure on the skin. Dermatographism usually goes away on its own without treatment in a short amount of time.
Temperature-induced hives
People who are sensitive to changes in temperature can sometimes get hives when the temperature changes. Hives can be brought on by cold water or air, and hives can be brought on by exercise if the body heats up too much. Some people can also get solar hives from being in the sun or in tanning beds.
Infection-induced hives
Both viral and bacterial infections can give you hives. Urinary tract infections and strep throat are two common bacterial infections that can cause hives. Hives are often brought on by the same viruses that cause infectious mononucleosis, hepatitis, and colds.
Finding relief: Treatment options
First, you have to figure out if you have hives before you can get treatment. Most of the time, your doctor will be able to tell if you have hives just by looking at you. If you have hives, your skin will show signs of the welts that come with them. Your doctor may also check your blood or skin to find out what caused your hives, especially if they were caused by an allergic reaction.
If you have mild hives that aren’t caused by allergies or other health problems, you might not need to see a doctor. In this case, your doctor might tell you to get short-term relief by:
- using antihistamines like diphenhydramine or cetirizine
- try not to irritate the area
- avoid hot water, which could make the hives worse.
- Getting into a cool or warm bath with colloidal oatmeal or baking soda
Anaphylaxis is a serious medical emergency that needs to be taken care of right away by a doctor.
Can hives be prevented?
You might be able to stop getting hives again in the future by making simple changes to the way you live. If you have allergies and you know what things are likely to make you sick, your doctor will tell you to stay away from these things as much as possible. You might also be able to reduce the chance of getting hives again by getting allergy shots.
If you just got hives, don’t go to places with a lot of humidity or wear clothes that are too tight.
What to expect
Even though hives can be itchy and uncomfortable, they are usually not too bad and go away after a while. But keep in mind that as some hives disappear, new ones might appear.
People don’t need to worry about mild cases of hives. If you have a severe allergic reaction and your throat is swelling, hives can be dangerous. If you have a severe case of hives, you should get help right away.










Leave a Reply