Cellulitis: Everything You Need to Know
Cellulitis is a common skin infection caused by bacteria. It can make the skin hurt and change colour. If the infection isn’t treated, it can spread to other parts of the body and lead to serious problems.
In fact, over 14 million people in the United States get cellulitis every year. The infection can happen anywhere on the body, and if it’s not treated, it can lead to serious problems.
In this article, we talk about what causes cellulitis, how to treat it, and what it feels like. Learn more by reading on.
What is cellulitis?
Cellulitis is an infection of the skin that can hurt a lot. At first, it may look like a discoloured, swollen spot that is hot and painful to touch. The swelling and discoloration can spread quickly.
Cellulitis tends to look red or pink on lighter skin tones. It might look dark brown, grey, or purple on darker skin tones.
Most often, it happens on the feet and lower legs, but it can happen anywhere on the body or face.
Cellulitis affects the skin and the tissues underneath it. The infection can move to your bloodstream and lymph nodes.
Cellulitis could be dangerous to your life if you don’t treat it. If you have symptoms, you need to see a doctor right away.
What causes cellulitis?
Cellulitis happens when a break in the skin lets certain kinds of bacteria in. Cellulitis is commonly caused by bacteria like Staphylococcus and Streptococcus (strep).
Cellulitis can start with wounds on the skin, like:
- cuts
- bug bites
- surgical wounds
What are the risk factors for cellulitis?
Several things increase your risk of getting cellulitis.
For example, you are more likely to get cellulitis if you have eczema or athlete’s foot. This is because these conditions can cause cracks in your skin that bacteria can get into.
If your immune system is weak, you are also more likely to get cellulitis because it can’t protect you as well from the infection.
Other things that put you at risk are:
- a cut, scrape, or other injury to the skin
- diabetes
- swelling in your arms or legs (lymphedema)
- obesity
What are the symptoms of cellulitis?
Some signs of cellulitis are:
- pain and tenderness in the affected area
- redness or inflammation of your skin
- a skin sore or rash that grows quickly
- tight, glossy, swollen skin
- a feeling of warmth in the affected area
- an abscess with pus
- fever
Some of the more serious signs of cellulitis are:
- shaking
- chills
- feeling ill
- fatigue
- dizziness
- lightheadedness
- muscle aches
- warm skin
- sweating
If you don’t treat cellulitis, it can spread to other parts of your body. If it does spread, you might start to feel some of the following:
- drowsiness
- lethargy (fatigue)
- blisters
- red or dark brown streaks on the skin
If you think you might have cellulitis, call your doctor right away.
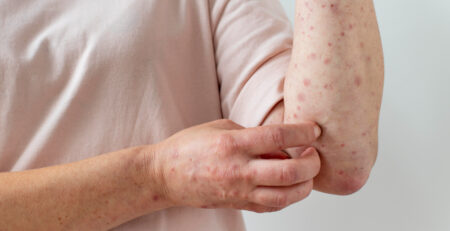
Pictures of cellulitis
Cellulitis can look different depending on how bad it is and where it is. Cellulitis is shown in the pictures
Is cellulitis contagious?
Most of the time, cellulitis doesn’t spread from one person to another. If you have an open cut on your skin and it touches an infected area, you could get a bacterial skin infection.
If you get cellulitis from an infection you got from someone else, it could be dangerous if you don’t treat it right away. This is why it’s important to tell your doctor about cellulitis symptoms as soon as you notice them.
Are there complications of cellulitis?
If you don’t treat cellulitis, it can lead to serious problems. Some things that can go wrong are:
- severe tissue damage (gangrene)
- amputation
- damage to internal organs that become infected
- septic shock
- death
How is cellulitis diagnosed?
Cellulitis is usually easy for your doctor to tell just by looking at your skin. A physical exam might reveal:
- swelling of the skin
- redness and warmth of the affected area
- swollen glands
Depending on how bad your symptoms are, your doctor may want to keep an eye on the affected area for a few days to see if the swelling and discoloration spread. In some cases, your doctor may test for bacteria by taking a sample of blood or the wound itself.
How is cellulitis treated?
Cellulitis is usually treated with antibiotics that are taken by mouth for a minimum of 5 days. Your doctor might also give you painkillers. But in some cases, doctors will give antibiotics through intravenous (IV) antibiotics as soon as they notice symptoms.
You should stay in bed until you feel better. Putting the swollen part of your body higher than your heart can also help.
If you start taking antibiotics, cellulitis should go away in 7 to 10 days. If your infection is bad, you might need to take medicine for a longer time.
Even if your symptoms get better in a few days, you must finish all of the antibiotics your doctor gives you.
When to contact a doctor
Contact your doctor if you:
- if you don’t feel better 3 days after starting antibiotics,
- your symptoms get worse,
- you get a fever,
- or you don’t feel better at all.
You may need to get antibiotics through an IV in a hospital if you:
- a high temperature
- low blood pressure
- an infection that doesn’t improve with oral antibiotics
- a weakened immune system due to other diseases
Surgery options
Most of the time, an infection will go away after a course of antibiotics. If you have an abscess, on the other hand, a doctor may need to drain it.
Before surgery to drain the abscess, the area is numbed with medicine. Then, the surgeon makes a small cut in the abscess to let the pus drain out.
The wound is then covered with a bandage so that it can heal. After that, you might have a small scar.
Home remedies
If you think you might have cellulitis, you should always see your doctor first. If you don’t treat it, it can spread and cause an infection that could kill you.
But you can do things at home to help with pain and other symptoms. You can start by cleaning the area of skin where you have cellulitis. Ask your doctor how to clean and cover the wound the right way.
For example, if your leg hurts, lift it higher than your heart. This will help get rid of pain and reduce swelling.
How long does it take to recover from cellulitis?
During the first 48 hours, you may feel worse. But two to three days after you start taking antibiotics, they should start to get better.
You should always take all of the antibiotics that your doctor gives you.
Keep the wound clean while you’re getting better. Follow your doctor’s advice about how to wash and cover the area of skin that is hurt.
Can you prevent cellulitis?
If your skin is broken, clean it right away and put antibiotic ointment on it. Cover your wound with a bandage and some medicine until it’s completely better. Every day, change the bandage.
Watch your wounds for changes in colour, pain, or drainage. This could mean that you have an infection.
If you have poor circulation or a condition that makes you more likely to get cellulitis, take these steps:
- Don’t let your skin dry out or it will crack.
- Conditions like athlete’s foot that cause skin to crack should be taken care of right away.
- Wear safety gear when you go to work or play sports.
- Check your feet every day for signs of damage or illness.
What other conditions may be confused with cellulitis?
There are many conditions that can cause symptoms that look like cellulitis.
Cellulitis vs. venous stasis
The National Eczema Association says that venous stasis causes skin to swell and change colour, and it can lead to skin ulcers. It happens when the blood flow in the lower legs and feet isn’t good, and it usually affects the lower legs and feet.
This condition is different from cellulitis in that it can happen on both sides of the body and is not caused by a bacterial infection. But if you have sores or ulcers because of venous stasis, you are more likely to get a skin infection.
Cellulitis vs. erysipelas
Erysipelasis another infection of the skin. It can start from open wounds, burns, or surgical cuts, just like cellulitis.
Usually, the infection is caused on the legs. It can happen less often on the face, arms, or trunk (torso).
Cellulitis, on the other hand, affects deeper tissue, while erysipelas is often caused by strep bacteria and affects the skin more.
Erysipelas also has these other symptoms:
- fever
- headache
- nausea
- chills
- weakness
- ill feeling
Antibiotics, most often penicillin or a drug like it, are used to treat erysipelas.
Cellulitis vs. abscess
An abscessis a swollen, pus-filled pocket under the skin. It happens when bacteria, usually Staphylococcus, get into your body through a cut or other open wound.
Your immune system sends white blood cells to fight the bacteria when this happens. The attack can make a hole in your skin that pus will fill up. There are dead cells, bacteria, and white blood cells in the pus.
abscess is not the same as cellulitis looks like a bump on the body. You might also have a fever and the chills.
Some abscesses go away on their own without having to be treated. In some cases, you may require antibiotics.Abscesses usually need to open and drain to get better.
Cellulitis vs. dermatitis
Dermatitis is a broad term for a rash that can be caused by many different things. These things are:
- atopic dermatitis (eczema)
- contact dermatitis, an allergic reaction to an irritating substance
Most types of dermatitis are not caused by bacterial infections like cellulitis is.
Common signs of dermatitis are:
- discolored skin
- blisters that ooze or crust
- itching
- swelling
- scaling
Dermatitis is a skin condition that causes swelling and itching. Antihistamines and cortisone creams are used by doctors to treat it. You will also need to stay away from the thing that made the reaction happen.
Cellulitis vs. DVT
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a clot of blood that forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs. A DVT can get if you sit or lie down for a long time, like on a long flight or after surgery.
Some signs of DVT are:
- pain in the leg
- redness
- warmth
If you have DVT, it’s important to see a doctor. If the clot breaks off and travels to the lungs, it can cause a condition called pulmonary embolism, which can be fatal pulmonary embolism (PE).
Blood thinners are used to treat DVT. These keep the clot from getting bigger and keep you from getting more clots.
Takeaway
Cellulitis is a common skin infection caused by bacteria that causes pain, swelling, and discoloration of the skin. Complications are uncommon, but they can be very bad. If you think you have cellulitis, you should always call your doctor.
Most people who have cellulitis get better after taking antibiotics for 7 to 10 days. Cellulitis can lead to gangrene or septic shock if it is not treated, and severe cases may need surgery.
Cellulitis is something that can happen again. Keep your skin clean if you get a cut or other open wound. This will help you avoid getting this infection. If you aren’t sure how to take care of your skin after it has been hurt, ask your doctor.






Leave a Reply