Hyperglycemia: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
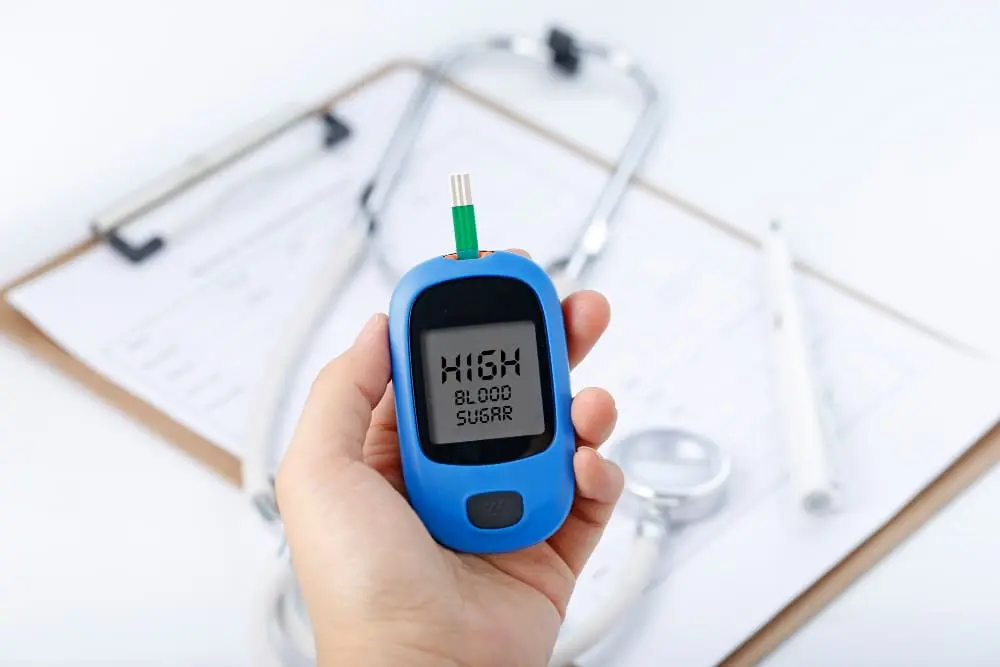
Hyperglycemia, commonly known as high blood sugar, occurs when there is an excessive amount of glucose circulating in the bloodstream. It is a hallmark of diabetes mellitus and can lead to serious health complications if not managed properly. This article explores the causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies for hyperglycemia.
Understanding Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia occurs when the body cannot properly utilize glucose due to insufficient insulin production or insulin resistance. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps regulate blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells for energy production. When this process is impaired, glucose accumulates in the bloodstream, leading to hyperglycemia.
Causes of Hyperglycemia
Several factors can contribute to hyperglycemia:
Diabetes Mellitus: Type 1 diabetes results from autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, while type 2 diabetes develops due to insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion.
Poor Diet: Consuming excessive carbohydrates or sugary foods can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, contributing to hyperglycemia, especially in individuals with diabetes.
Lack of Physical Activity: Regular exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake, reducing the risk of hyperglycemia.
Medication: Certain medications, such as corticosteroids used to treat inflammatory conditions, can interfere with insulin function and lead to elevated blood sugar levels.
Stress: Stress hormones like cortisol can raise blood sugar levels, particularly in individuals predisposed to diabetes.
Symptoms of Hyperglycemia
Recognizing the symptoms of hyperglycemia is crucial for early intervention:
Increased Thirst: Excessive thirst (polydipsia) is a common early symptom of hyperglycemia as the body tries to flush out excess glucose through urine.
Frequent Urination: Elevated blood sugar levels prompt the kidneys to work harder to filter glucose, leading to increased urination (polyuria).
Fatigue: Insufficient glucose uptake by cells deprives the body of energy, causing fatigue and weakness.
Blurred Vision: High blood sugar levels can cause fluid to be pulled from the lenses of the eyes, affecting vision temporarily.
Slow Healing: Hyperglycemia impairs the body’s ability to heal wounds and infections due to poor circulation and compromised immune function.
Complications of Untreated Hyperglycemia
Persistent hyperglycemia can lead to serious complications over time:
Cardiovascular Disease: High blood sugar levels contribute to the buildup of fatty deposits in blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke.
Kidney Damage: Diabetes-related kidney disease (nephropathy) can progress to kidney failure if hyperglycemia is poorly controlled.
Neuropathy: Nerve damage caused by hyperglycemia can lead to pain, tingling, or numbness in the extremities (peripheral neuropathy).
Eye Problems: Hyperglycemia increases the risk of diabetic retinopathy, a leading cause of blindness in adults.
Management of Hyperglycemia
Effective management of hyperglycemia focuses on controlling blood sugar levels and minimizing the risk of complications:
Blood Glucose Monitoring: Regularly checking blood sugar levels helps individuals with diabetes adjust their treatment plan as needed.
Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fiber, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins helps regulate blood sugar levels and promotes overall health.
Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise improves insulin sensitivity and helps maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
Medication: Insulin therapy or oral medications prescribed by healthcare providers help manage blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes.
Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can help reduce stress levels and prevent spikes in blood sugar.
Preventing Hyperglycemia
Preventive measures can help individuals reduce the risk of hyperglycemia:
Education: Understanding the causes and symptoms of hyperglycemia empowers individuals to take proactive steps in managing their health.
Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and a balanced diet promotes stable blood sugar levels.
Regular Medical Check-ups: Routine visits to healthcare providers allow for early detection of diabetes or adjustments in treatment plans to prevent complications.
Conclusion
Hyperglycemia is a common concern for individuals with diabetes but can be managed effectively through lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring. By understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms early, and implementing appropriate management strategies, individuals can minimize the impact of high blood sugar levels on their health and well-being.