Rosacea: Types, Causes, and Remedies
What is rosacea?
Rosacea is a skin disease that lasts for a long time and affects more than 16 million Americans. No one knows what causes rosacea, and there is no treatment. But research has helped doctors find ways to treat the disease by making the symptoms less bad.
Rosacea comes in four different forms. The symptoms for each subtype are different. You can have more than one kind of rosacea at the same time.
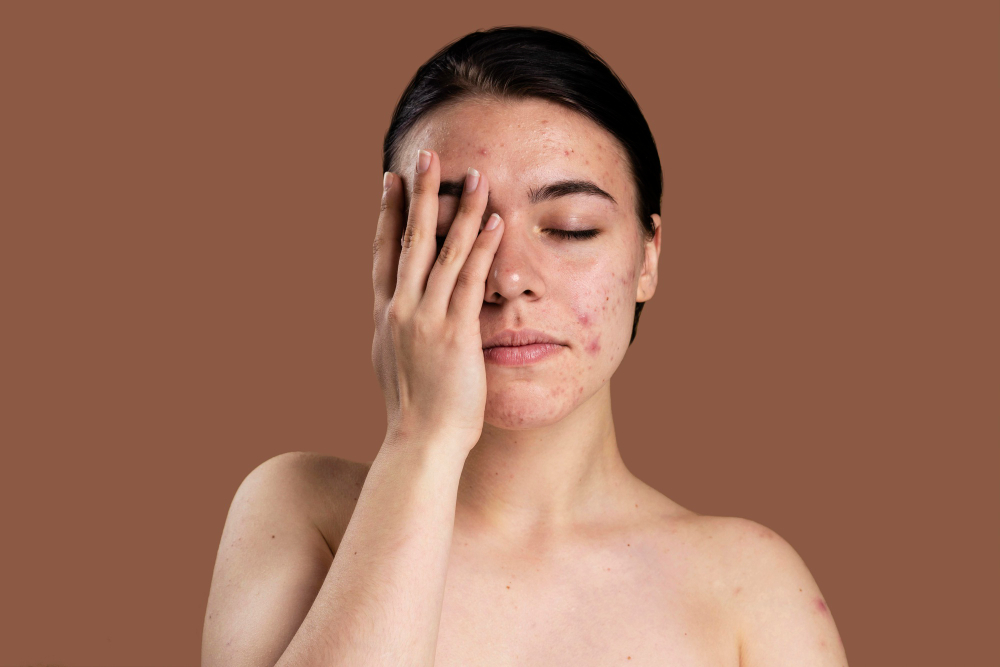
During flare-ups, small, red, pus-filled bumps appear on the skin. This is the most common sign of rosacea. Most of the time, rosacea only affects your nose, cheeks, and forehead.
Most flare-ups happen in cycles. This means that your symptoms will last for weeks or months at a time, go away, and then come back.
Types of rosacea
There are four kinds of rosacea:
- Subtype one, called erythematotelangiectatic rosacea (ETR), is marked by redness, flushing, and blood vessels that can be seen on the face.
- The second type, called papulopustular (or acne) rosacea, is often seen in middle-aged women and causes breakouts that look like acne.
- Rhinophyma, which is a rare form of subtype three, is a thickening of the skin on your nose. It usually happens to men, and it often goes along with another type of rosacea.
- The fourth type of rosacea is called ocular rosacea, and its symptoms are all around the eyes.
Symptoms of rosacea
Each type of rosacea has its own set of symptoms.
Signs of rosacea ETR:
- flushing and redness in the center of your face
- visible broken blood vessels
- swollen skin
- sensitive skin
- stinging and burning skin
- dry, rough, and scaly skin
Signs of acne rosacea:
- acne-like breakouts and very red skin
- oily skin
- sensitive skin
- broken blood vessels that are visible
- raised patches of skin
Signs of thickening skin:
- bumpy skin texture
- thick skin on nose
- thick skin on chin, forehead, cheeks, and ears
- large pores
- visible broken blood vessels
Signs of ocular rosacea:
- bloodshot and watery eyes
- eyes that feel gritty
- burning or stinging sensation in the eyes
- dry, itchy eyes
- eyes that are sensitive to light
- cysts on eyes
- diminished vision
- broken blood vessels on eyelids
What causes rosacea?
No one knows what makes rosacea happen. It could be caused by both genetics and the environment. Some things are known to make rosacea symptoms worse. These things are:
- eating foods with heat
- Cinnamon, chocolate, tomatoes, and citrus all have a chemical called cinnamaldehyde in them.
- Helicobacter pylori bacteria in the gut from drinking hot coffee or tea
- a skin mite called demodex eating foods with heat
- Cinnamon, chocolate, tomatoes, and citrus all have a chemical called cinnamaldehyde in them.
- bacteria in the gut from drinking hot coffee or tea
Risk factors for rosacea
Some things will make it more likely that you will get rosacea than others. Rosacea usually happens to people between 30 and 50 years old. People with fair skin, blonde hair, and blue eyes are more likely to have it.
Rosacea can also be caused by genes. If you have Celtic or Scandinavian ancestors or if someone in your family has rosacea, you are more likely to get it. Women are also more likely than men to get the disease. But when men get the disease, their symptoms are often worse.
How do I know if I have rosacea?
Your doctor can easily tell if you have rosacea by looking at your skin. They might tell you to see a dermatologist, who can figure out if you have rosacea or some other skin problem.
How can I control my symptoms?
Rosacea can’t be cured, but there are things you can do to manage its symptoms.
Make sure to take care of your skin by using gentle cleansers and products that don’t contain oil but are made with water.
Don’t buy products that:
- alcohol
- menthol
- witch hazel
- exfoliating agents
Some of these ingredients might make your symptoms worse.
Your doctor will work with you to come up with a plan for how to treat you. Most of the time, this is done with antibiotic creams and antibiotic pills.
Write down everything you eat and everything you put on your skin. This will help you find out what makes your symptoms worse.
Other management steps include:
- staying out of the sun and putting on sunscreen
- Lasers and light treatments can help with some severe cases of rosacea if you don’t drink alcohol and stay away from it.
- Taking eye medicines and antibiotics for ocular rosacea and microdermabrasion to thin out thickening skin
Coping with rosacea
Rosacea is a long-term skin condition that you will have to learn to deal with. Having a long-term illness can be hard to deal with. Find help by going to online message boards or support groups. When you talk to other people with rosacea, you may feel less alone.
Long-term outlook for rosacea
Rosacea can’t be cured, but it can be controlled with medicine. Rosacea affects different people in different ways, and it can take time to figure out how to treat it. Working with your doctor to make a treatment plan and avoiding your triggers is the best way to stop an outbreak.









Leave a Reply